In the contemporary global landscape characterized by growing interconnectivity, the scope of our digital footprints is continuously rising, therefore generating a comprehensive dataset that can be readily monitored and scrutinized by diverse organizations. The increasing apprehension about internet privacy has stimulated the need for technologies that enable folks to reestablish authority over their digital data. The anti-detect browser has garnered considerable attention in recent years as a notable technology.
The Use of Anti-Detect Browsers for Protecting Digital Identities
Anti-detect browsers refer to a category of web browsers that are specifically engineered to reduce the digital traces left by individuals, hence concealing their online behaviors from intrusive surveillance. In contrast to traditional web browsers, which generate a distinct identifier called a browser fingerprint, anti-detect browsers use several methods to obscure this fingerprint. As a result, websites and trackers have challenges in precisely identifying and creating profiles for individual users.

Exploring the Inner Workings: Approaches to Concealing Data
Anti-detect browsers use a variety of advanced strategies in order to accomplish their objectives of increasing user privacy. The aforementioned methods encompass:
User Agent Spoofing
User agent spoofing refers to the act of altering the user agent string, which is responsible for identifying the user’s browser and operating system, with the intention of generating a fabricated identity and deceiving tracking mechanisms.
Browser Fingerprinting Modification
Modification of Browser Fingerprinting: The act of modifying different parameters inside a web browser, including but not limited to font rendering, time zone, and language settings, with the intention of producing a distinct fingerprint that diverges from the typical user profile.
VPN Integration
The process of VPN integration involves the incorporation of virtual private networks (VPNs) into a system, which serves to conceal the user’s actual IP address and redirect internet traffic via a distant server. This additional step enhances the concealment of the user’s location and online activity.
Blocking and Modifying Browser Features
The act of blocking or changing certain browser capabilities, such as JavaScript, cookies, and browser plugins, serves the purpose of preventing the tracking of user activity and the collection of sensitive information.

The Data Privacy Landscape: A Growing Demand for Protection
Anti-detect browsers may be categorized under the wider scope of Data Privacy Tools, which refers to a meta trend including several software and services aimed at safeguarding users’ privacy in the digital domain. Online privacy is regarded as a significant concern by 9 out of 10 Americans. The increasing need for data privacy technologies is driven by many factors:
Increased Awareness of Online Tracking
The growing recognition of internet tracking has led to an elevated level of anxiety among people over the protection of their personal data and privacy. In fact, searches for “data privacy tools” have grown by 200% over the past five years.
Legal and Regulatory Changes
Legal and regulatory changes have been introduced by governments globally, with the aim of imposing more stringent data privacy restrictions. One notable example is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, which empowers people with more authority over their personal data.
Data Breaches and Privacy Scandals
The occurrence of data breaches and privacy scandals of significant magnitude has exacerbated the erosion of public confidence in the manner in which firms manage personal data. Consequently, there is now a heightened need for more comprehensive privacy protection mechanisms.
Examples of In-Demand Data Privacy Tools
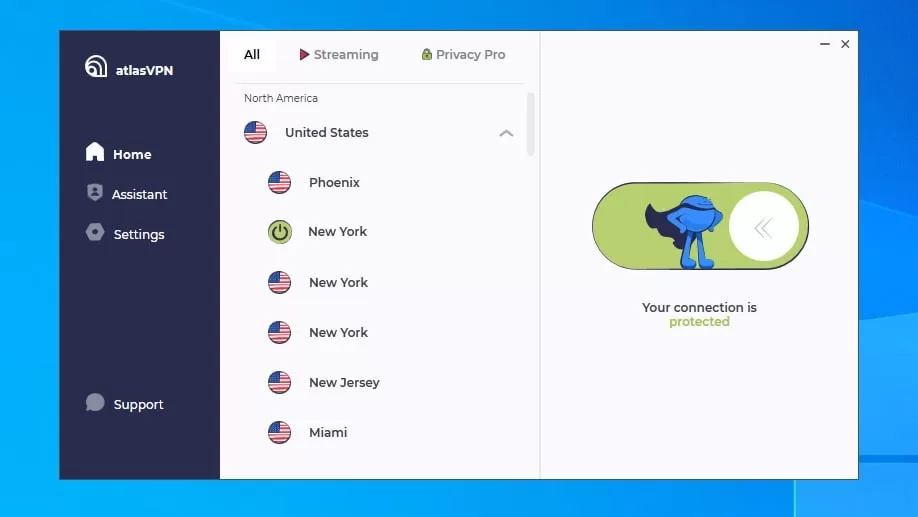
Atlas VPN
Atlas VPN is a virtual private network (VPN) that encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a server in a different location. This makes it more difficult for hackers and other third parties to track your online activity. Atlas VPN uses “military-grade encryption,” which is the same type of encryption that is used by the military to protect sensitive information.
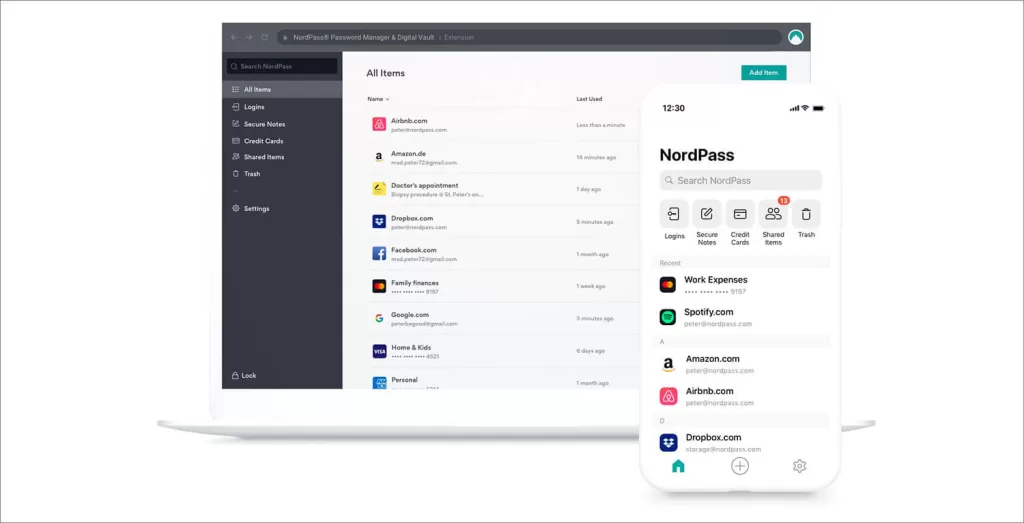
NordPass
NordPass is an encrypted password vault that allows you to store and manage your passwords securely. NordPass uses “zero-knowledge encryption,” which means that only you have the ability to decrypt your passwords. This means that NordPass cannot access your passwords, even if they are subpoenaed by a court of law.
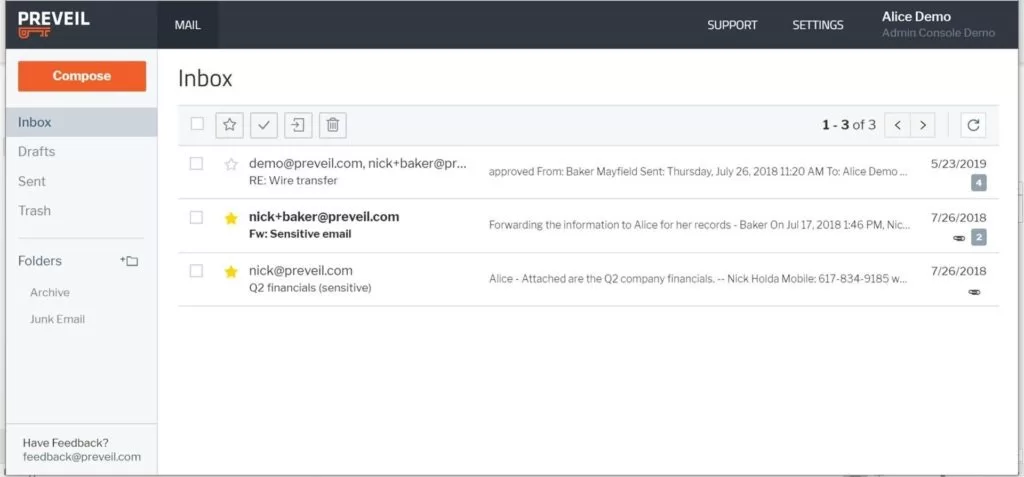
PreVeil
PreVeil is a B2B encrypted email, file-sharing, and messaging service. PreVeil uses end-to-end encryption, which means that your messages can only be read by the intended recipient. PreVeil also offers a number of other security features, such as two-factor authentication and encrypted attachments.
All of these tools can help you to protect your privacy online. However, it is important to remember that no tool is foolproof. You should always take steps to protect your privacy, such as using strong passwords and being careful about what information you share online.
Conclusion: Empowering Individuals in the Digital Age
The use of anti-detect browsers, in conjunction with other data privacy solutions, is enabling people to exert enhanced authority over their digital identities and safeguard their privacy within a swiftly changing online environment. The increasing advancement of technology and the growing sophistication of monitoring tactics need the heightened significance of effective data privacy measures.